| Ch 3. Particle Energy Methods | Multimedia Engineering Dynamics | ||||||
|
Work & Energy |
Conservative Forces | Power & Efficiency | |||||
| Power and Efficiency: Velocities | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| - Particle - |
| 1. General Motion |
| 2. Force & Accel. |
| 3. Energy |
| 4. Momentum |
| - Rigid Body - |
| 5. General Motion |
| 6. Force & Accel. |
| 7. Energy |
| 8. Momentum |
| 9. 3-D Motion |
| 10. Vibrations |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Dynamics Eqs |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
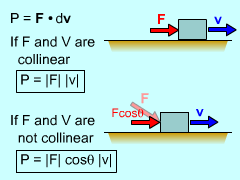 Direction of Force and Motion |
Power is the rate at which work is expended, P = ΔU/Δt = dU/dt Recall that work, dU, is simply the force through the distance. If the force is constant, the can be written as dU/dt = F · d(r)/dt or simply, Notice that the force and direction need to be parallel. The dot product forces the force vector and velocity vector to be parallel. |
||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Mechanical efficiency is the ratio of the "energy out" to the "energy in" of a system. This accounts for energy lost due to system in-efficiencies such as friction. Efficiency can also be written in terms of power, |
||||||||||||||||