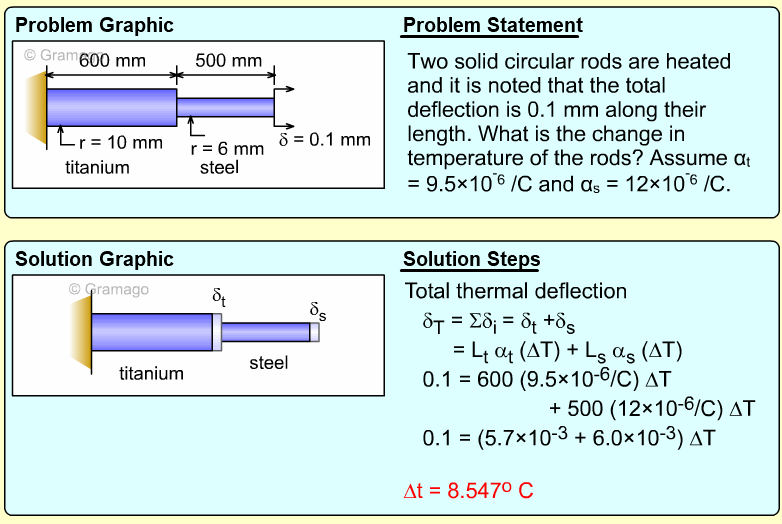
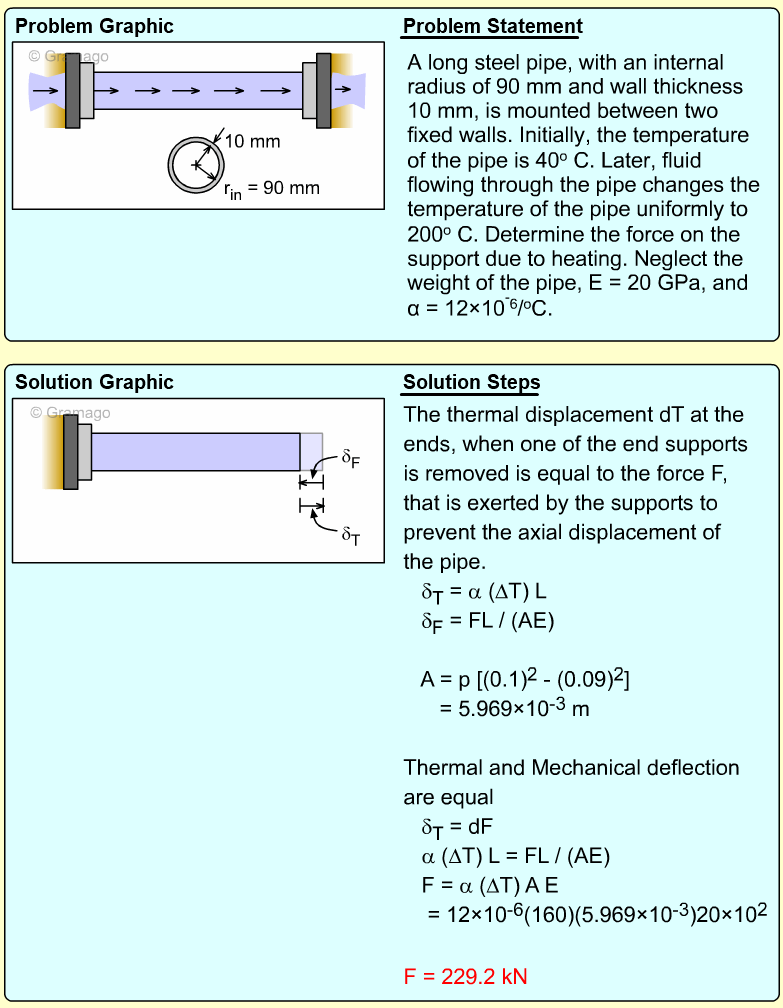
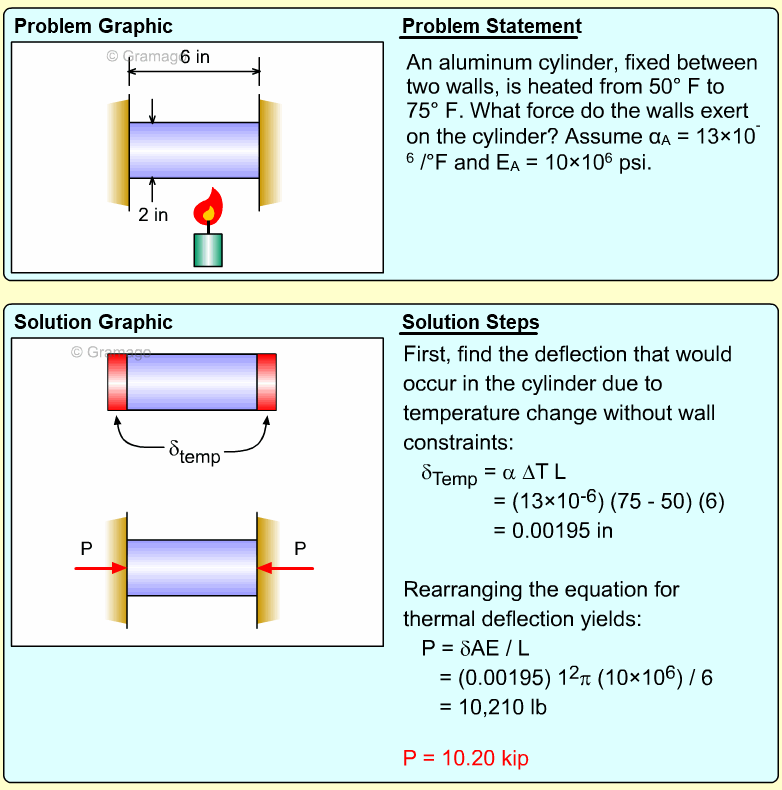
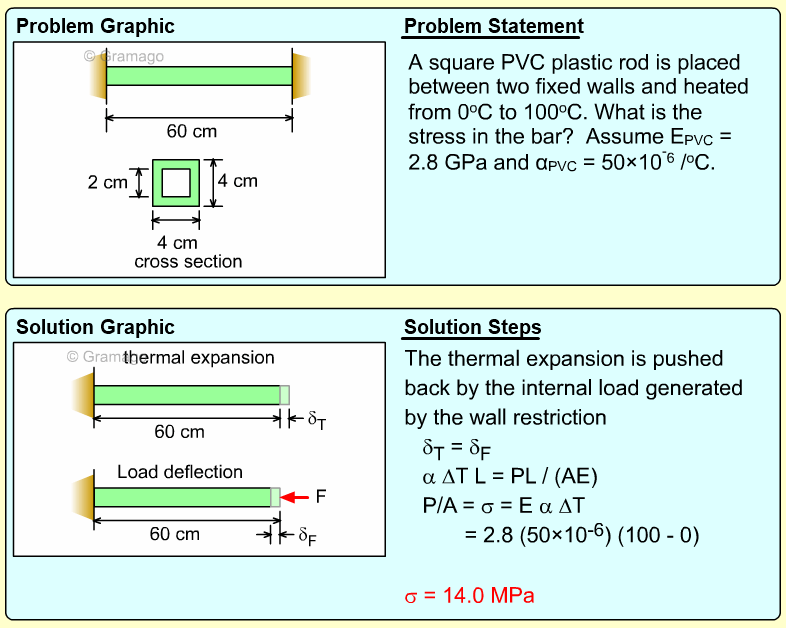
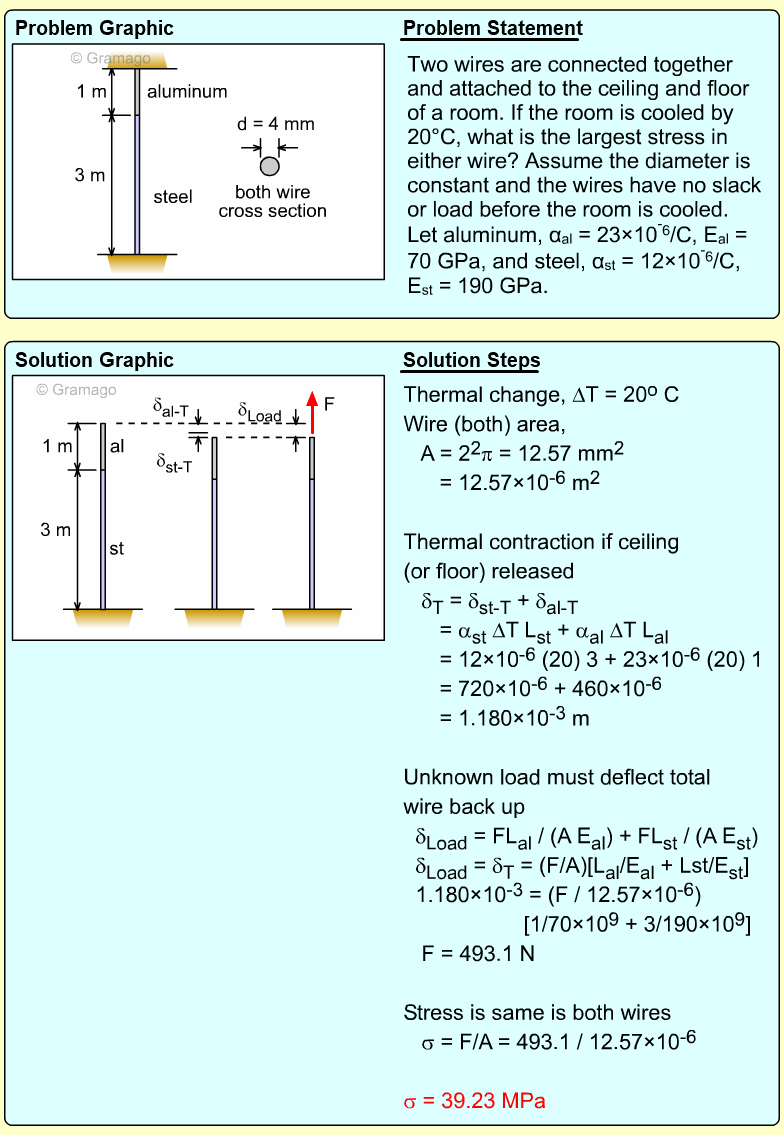
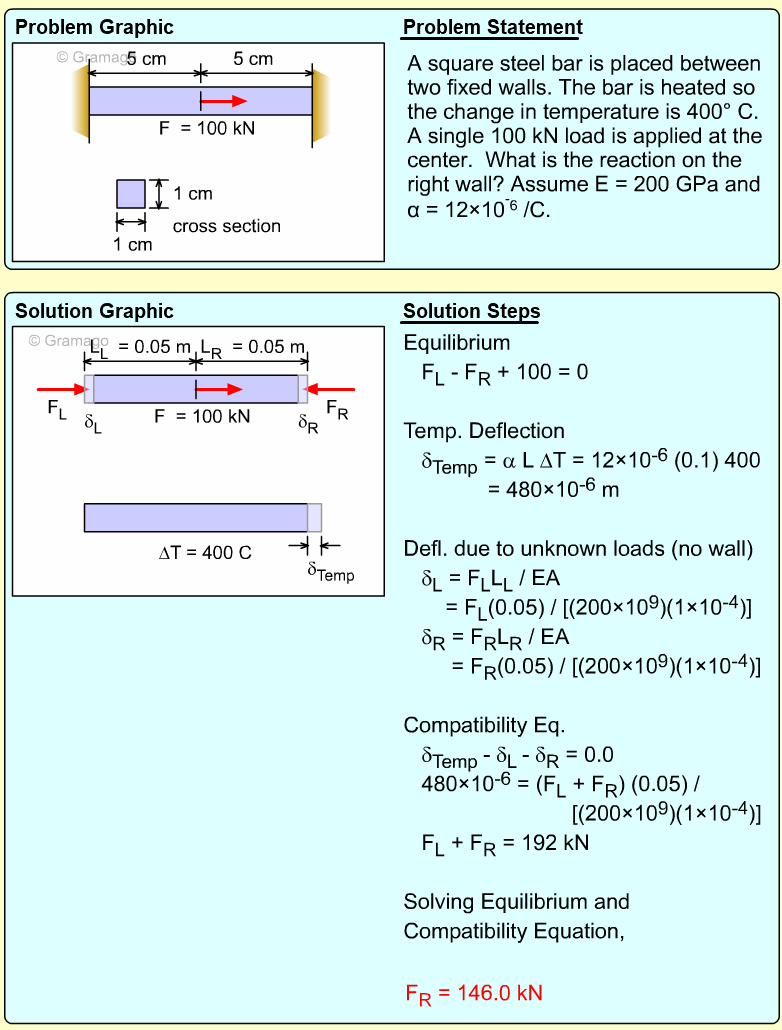
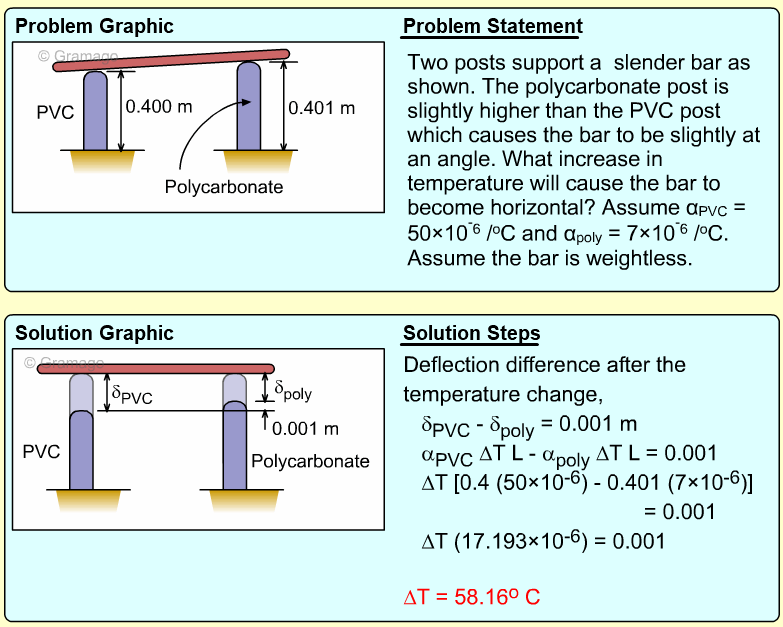
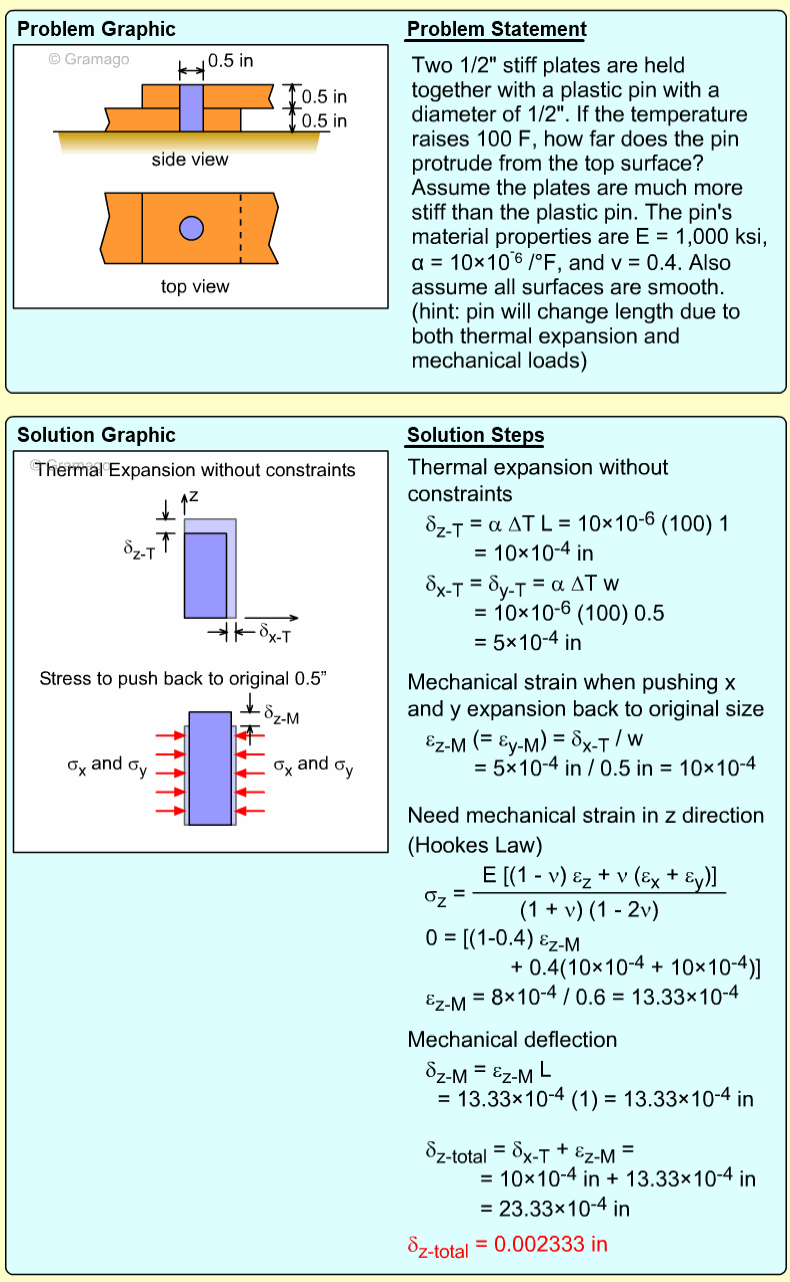
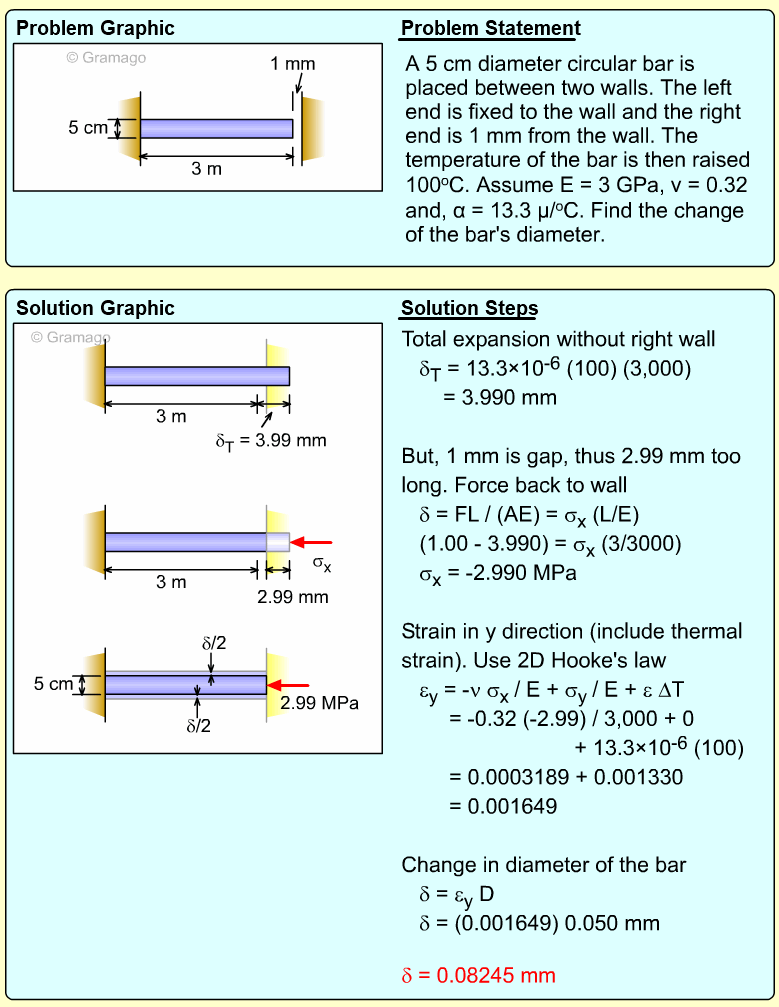
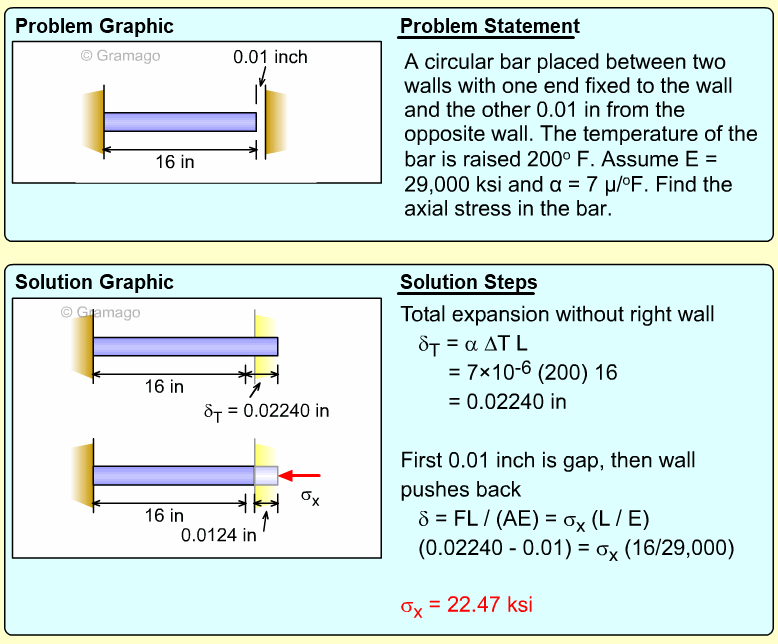
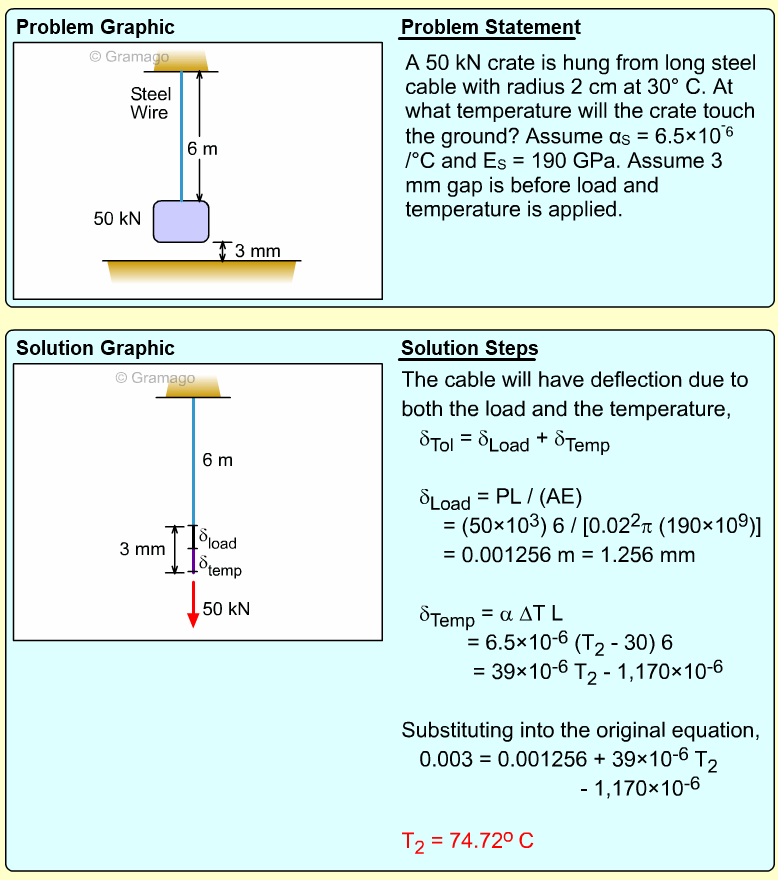
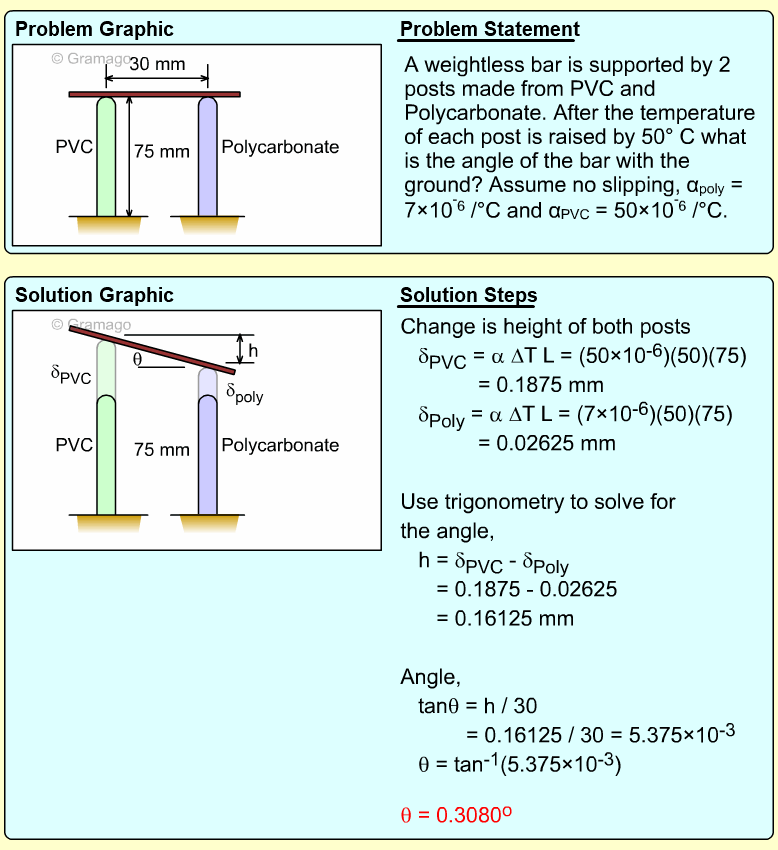
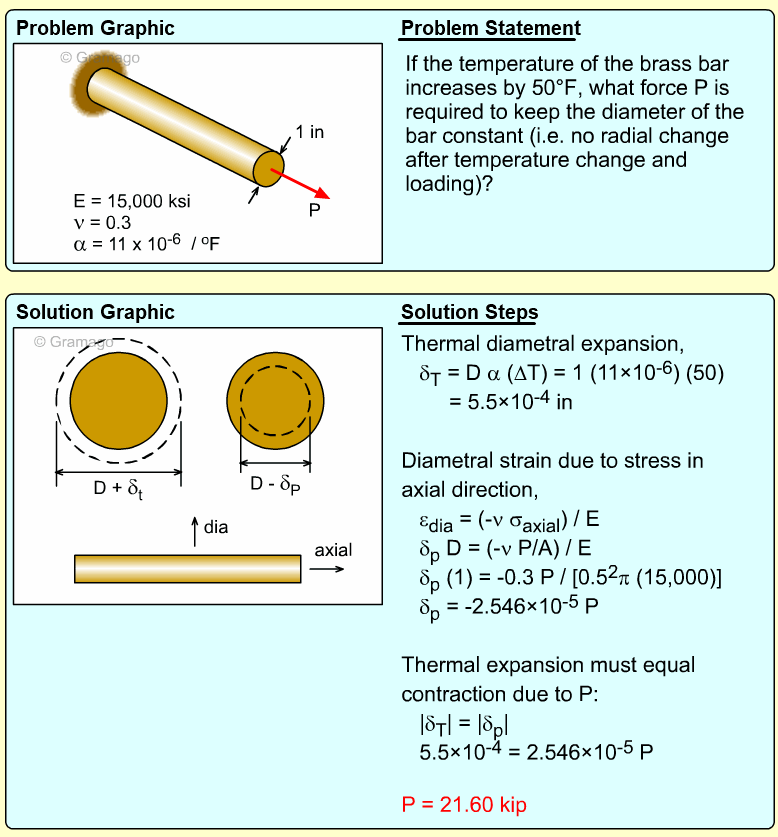
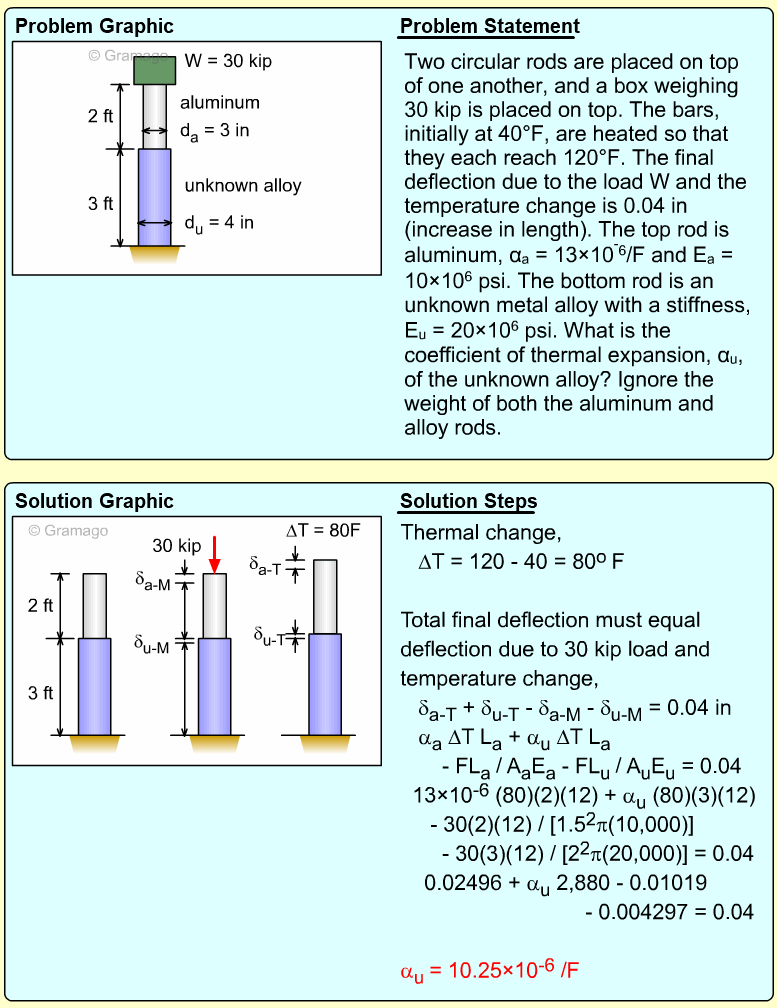
| Ch 1. Stress and Strain | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Normal Stress |
Shear and Bearing Stress |
Normal Strain |
Hooke's Law |
Thermal Effects |
Indeterminate Structures |
||
| Thermal Effects | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Example |
||
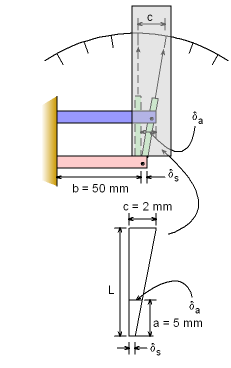
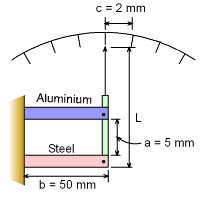 Schematic Diagram of the Thermometer at Room Temperature |
In a class project a student has decided to make a new type of thermometer. The thermometer assembly consists of two plates, one made of aluminum and the other made of steel. Both plates are the same length, b, at room temperature. When the temperature changes, the plates expand different, causing a pointer to rotate. Each increment on the scale corresponds to a temperature change of 1o F. The distance, c, on the scale is 2 mm which is very small when compared to the length, L, of the indicator, (c << L).The length of each plate, b, is 50 mm. What must be the length of the indicator? The thermal expansion of the indicator can be neglected. The thermal expansion of aluminum, αa, is 13×10-6/oF and that of steel, αs, is 6.5×10-6/oF. |
|
| Solution |
||
|
Since each plate is made of different materials their overall length change due to temperature change of 1oF is different. Recall, the distance between two consecutive pointer is very small compared to the length of the indicator. So, the length, c, can be assumed to be a straight line. Using similar triangles gives, |
|
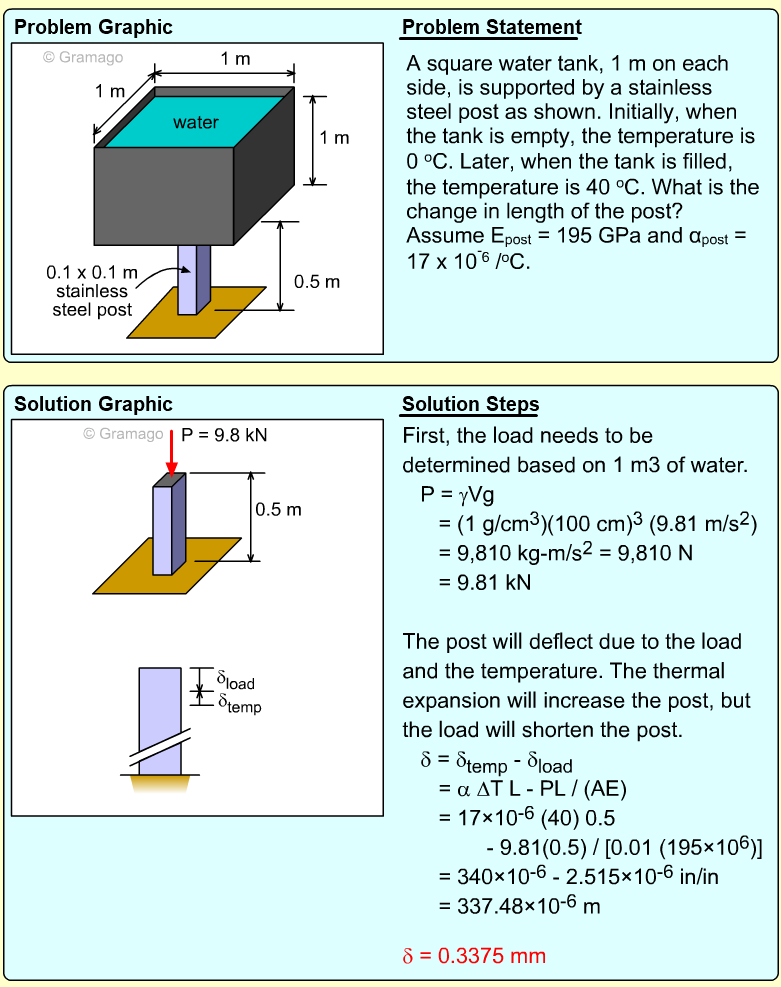
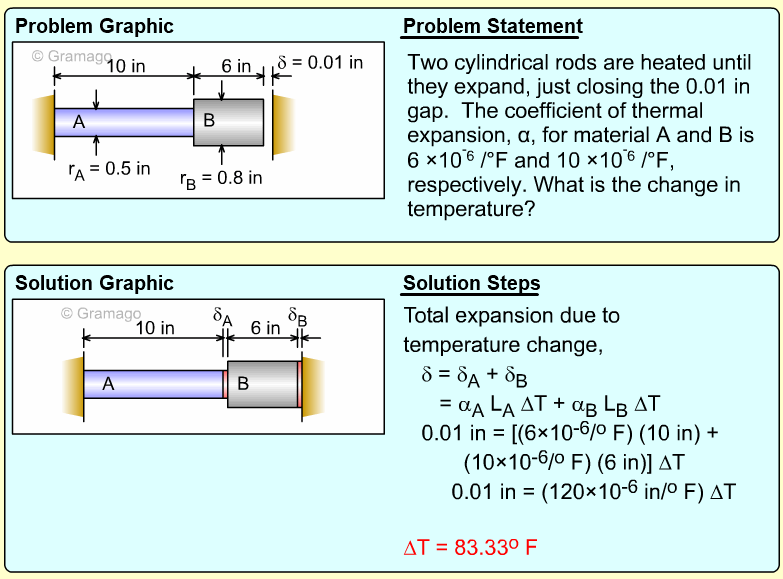
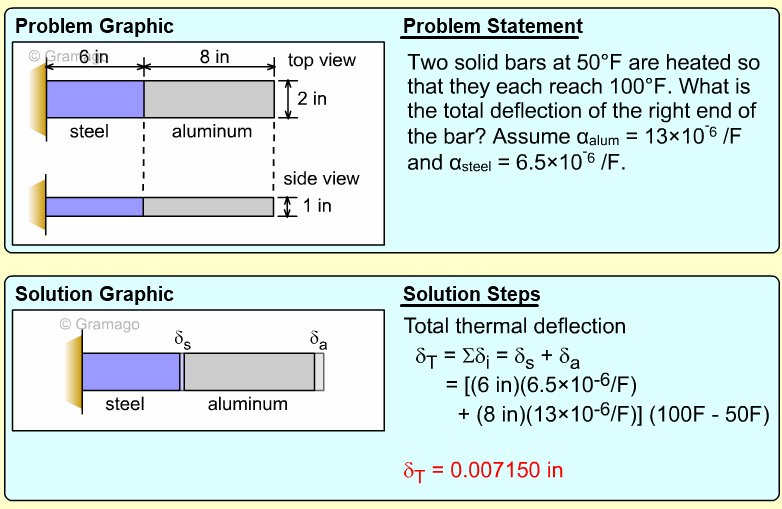
| Example Problem 1 |
||
|
||
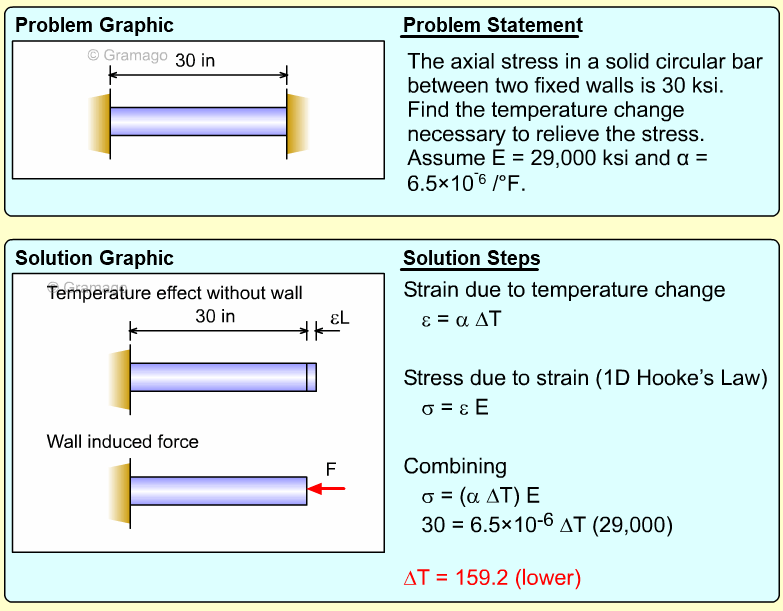
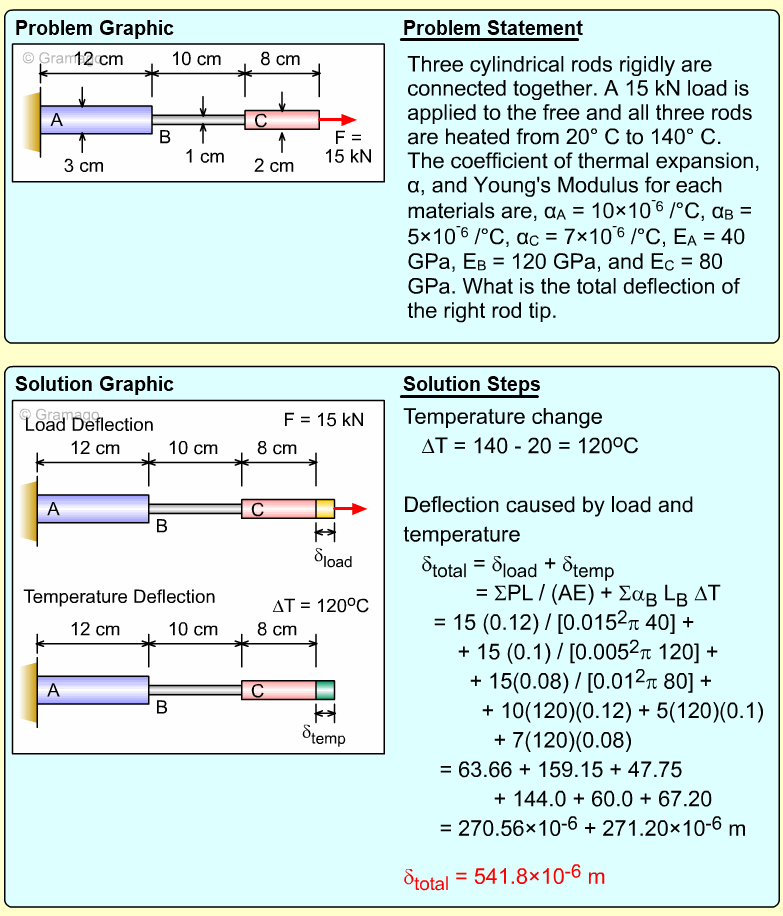
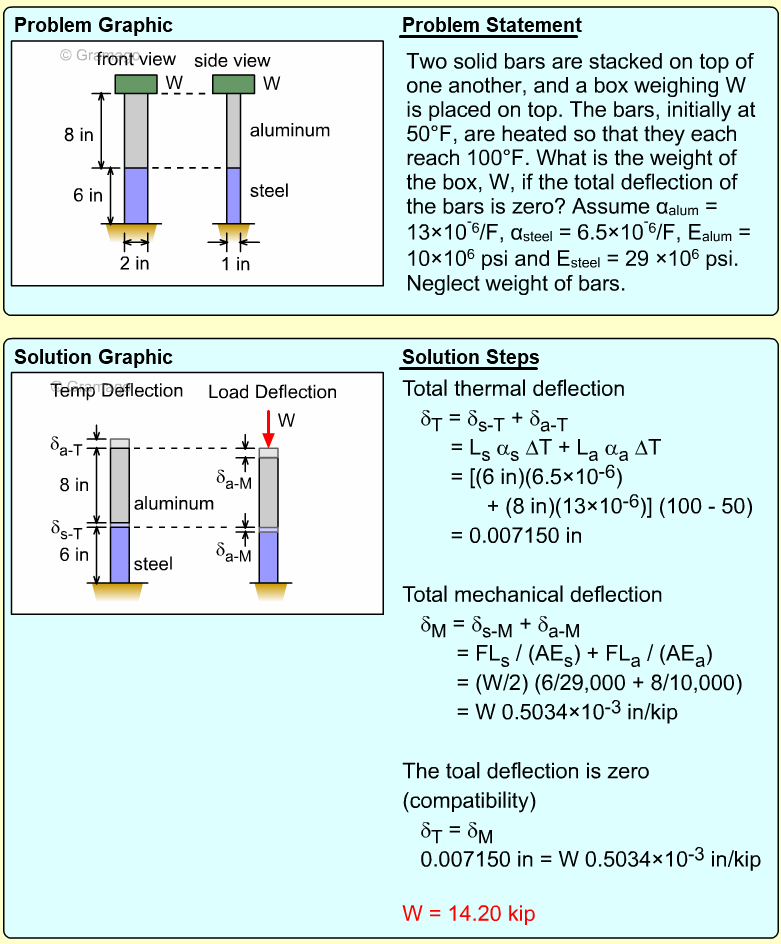
| Example Problem 2 |
||
|
||
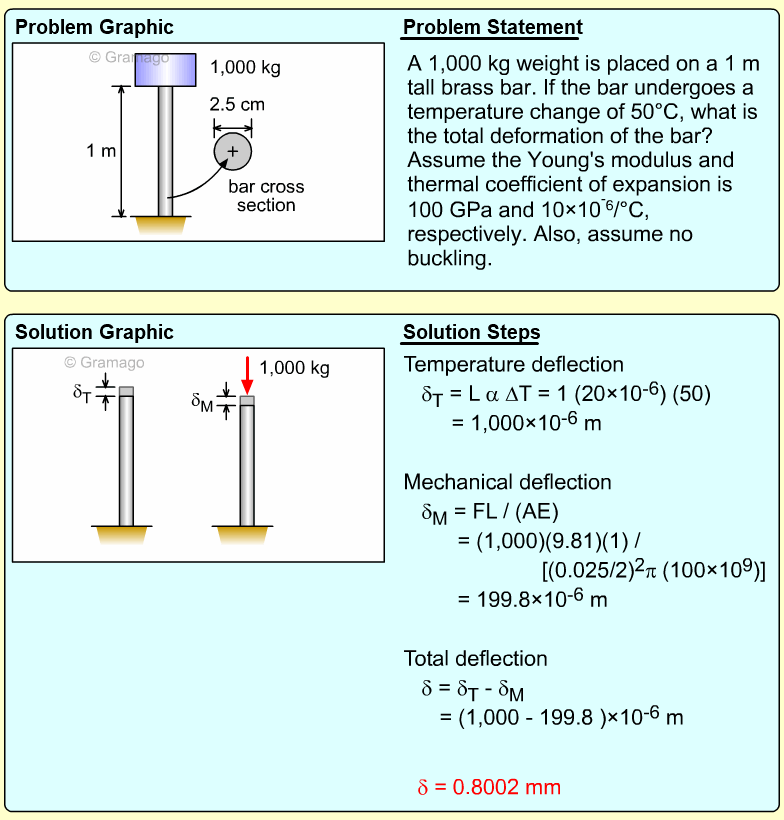
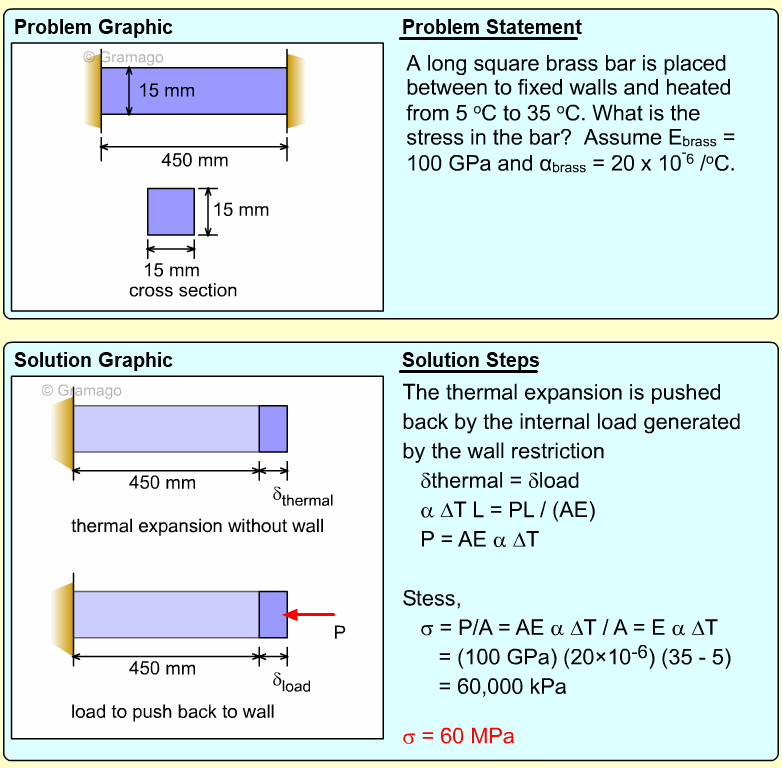
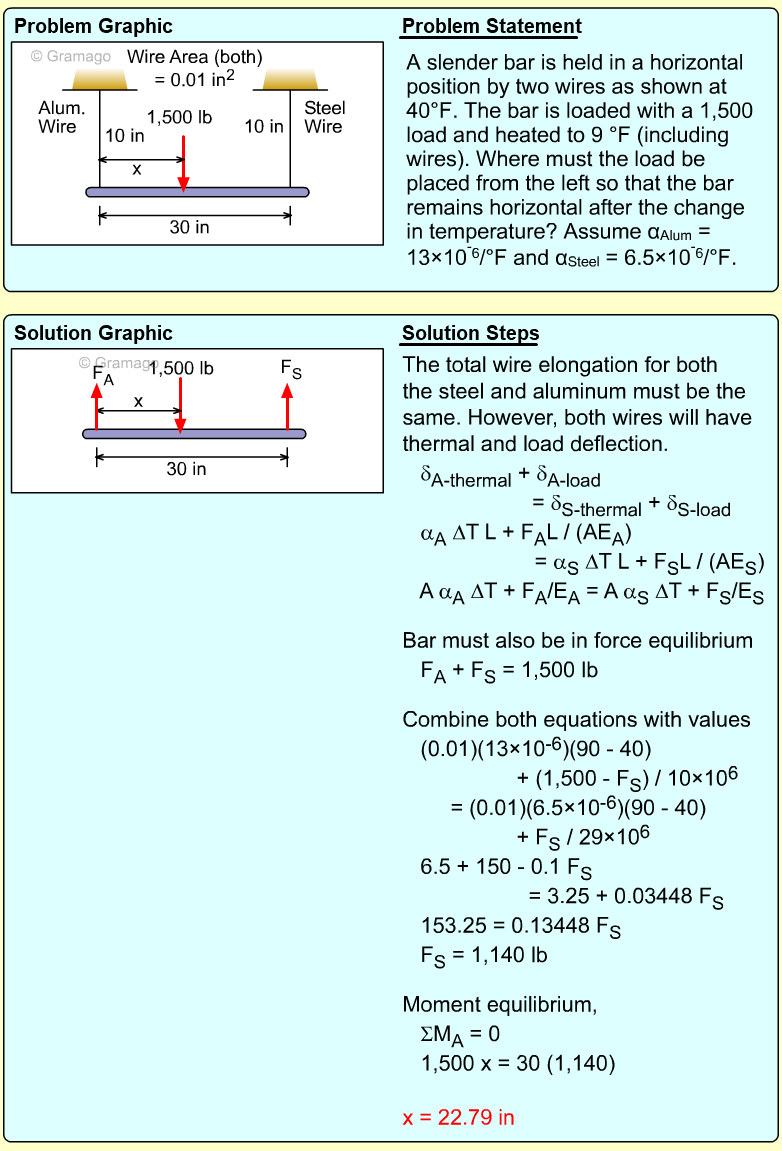
| Example Problem 3 |
||
|
||
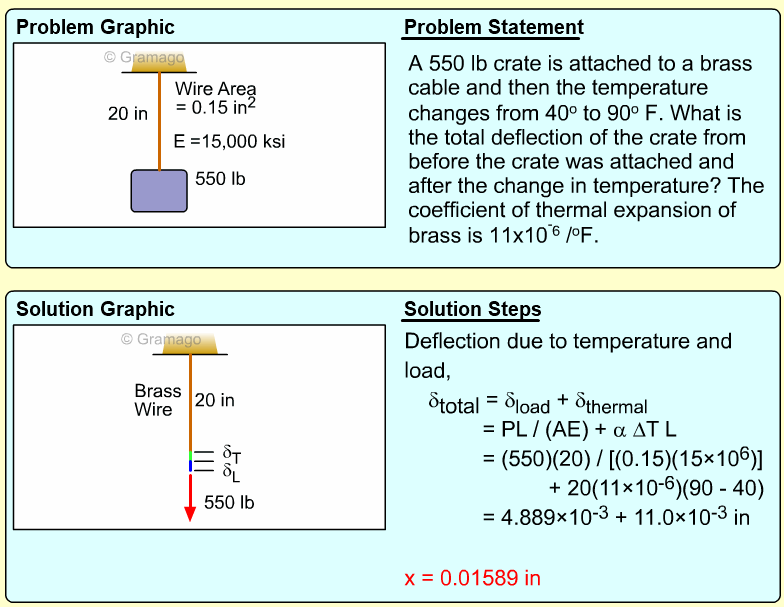
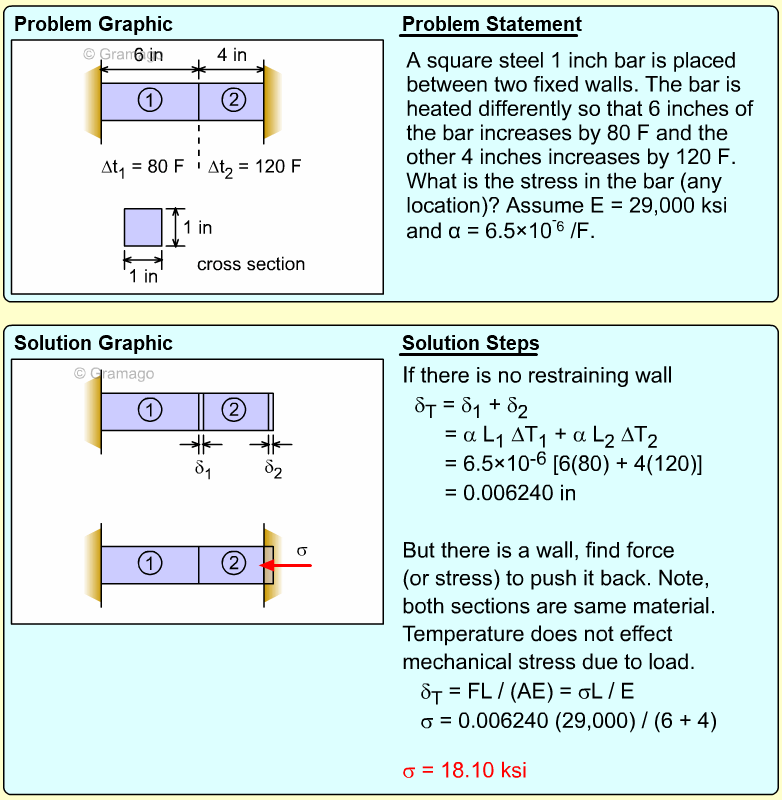
| Example Problem 4 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 5 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 6 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 7 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 8 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 9 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 10 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 11 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 12 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 13 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 14 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 15 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 16 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 17 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 18 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 19 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 20 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 21 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 22 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 23 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 24 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 25 |
||
|
||