| Ch 1. Basics | Multimedia Engineering Fluids | ||||||
|
Mass Density |
Ideal Gas Law |
Viscosity |
Surface Tension |
Vapor Pressure |
|||
| Surface Tension | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Fluid Statics |
| 3. Kinematics |
| 4. Laws (Integral) |
| 5. Laws (Diff.) |
| 6. Modeling/Similitude |
| 7. Inviscid |
| 8. Viscous |
| 9. External Flow |
| 10. Open-Channel |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Fluid Eqs |
| Water/Air Tables |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
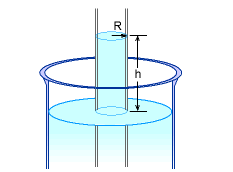 Capillary Action |
The height of the water column is given as a function of the contact angle (θ), radius of the tube (R), density (ρ) and surface tension (σ) of the liquid as follows: h = 2σcosθ / ρgR For water in contact with a clean glass, the contact angle is zero, hence the equation reduces to h = 2σ / ρgR For water at 30oC, the surface tension and density are 0.0712 N/m and 995.7 kg/m3 respectively, as noted in the theory page. For a tube with a radius of 1 mm: h = 2(0.0712)(106)/(995.7)(9.8)(1)
For a tube with a radius of 10 mm: h = 2(0.0712)(106)/(995.7)(9.8)(10)
Note that the water rise in the capillary tube decreases with an increase of the radius of the tube. |
|